October 22, 2025
– 9 minute read
Boost growth with a customer loyalty business model: retain clients, personalize experiences, reward engagement, and turn buyers into long-term brand advocates.

Cormac O’Sullivan
Author
Businesses must focus on keeping existing customers engaged and satisfied through a customer loyalty business model. Unlike basic loyalty programs, this approach integrates retention into every aspect of operations, from personalized experiences to data-driven strategies.
By understanding your customers, rewarding repeat purchases, and creating meaningful interactions, companies can transform casual buyers into long-term customers who drive steady revenue and promote the brand through word of mouth. While challenges exist, a well-executed loyalty model strengthens relationships, improves customer satisfaction, and builds lasting business growth.
Loyalty Business Model vs. Basic Loyalty Programs
Many businesses confuse loyalty programs with a true customer loyalty business model, but the difference is profound. Basic programs typically reward repeat purchases with points, discounts, or perks, often functioning as a short-term marketing tool. They focus on transactions rather than relationships and may drive temporary repeat business without building deeper engagement. A loyalty business model, by contrast, positions customer retention as the engine of growth.
Margins come from keeping long-term customers, not constantly acquiring new ones, making repeat purchases more valuable than high customer turnover. Loyalty is woven into every department from product development and service to sales and operations, ensuring the customer experience is consistent, meaningful, and aligned with expectations.
Decisions are guided by customer data, feedback, and insights, creating an environment where every touchpoint strengthens customer relationships. In essence, a loyalty business model transforms retention into strategy, making happy, engaged customers the core driver of sustainable profitability and growth.
The 5 Components of a Loyalty-Based Business
A true customer loyalty business model extends beyond marketing. It is embedded across every department, from customer service to product development, ensuring that every interaction strengthens relationships and encourages repeat purchases. The following five components highlight how businesses can design loyalty as a core operational principle.
1. Incentives and Reward Structures
Rewards remain a foundational element, but in a loyalty business model, they go beyond simple discounts. Effective incentives are meaningful, personalized, and aligned with what customers expect. They can include early access to products, exclusive experiences, or recognition for top long-term customers.
The key is to reinforce engagement without eroding margins. While rewards encourage repeat business, they are most effective when integrated with personalized service and ongoing communication, rather than acting as a stand-alone marketing tactic.
2. Scalable Personalized Customer Experiences
Customers respond strongly when businesses make them feel seen and valued. Personalization is not only about product recommendations it extends to service, communications, and experiences. Service teams can be trained to remember customer names, preferences, and past interactions, making each engagement feel human and attentive.
Frequent feedback loops, such as post-interaction surveys or check-ins, help ensure that these personal touches remain relevant and effective. This level of attention fosters trust, strengthens customer relationships, and encourages loyalty that goes beyond transactional rewards.
3. Service-Driven Organizational Culture
Building loyalty requires a service-first culture. Employees must be empowered and trained to act as loyalty ambassadors. This includes remembering customers’ names, preferences, and previous interactions, proactively resolving issues, and creating positive experiences at every touchpoint.
Regular training and frequent feedback loops ensure that service teams continuously improve and adapt to evolving customer expectations. When customers feel genuinely cared for, they are more likely to repeat purchases and recommend the brand, generating lasting word-of-mouth advocacy.
Customer-Centric Product Development
Product teams play a crucial role in loyalty by involving customers in the development process. Frequent research and feedback sessions allow businesses to align offerings with customer needs and expectations. For instance, companies like Fish Name Fred call their top 20 customers to preview new collections, gathering insights and making customers feel directly involved in shaping products.
This co-creation approach strengthens emotional bonds, encourages repeat business, and makes customers feel like partners rather than mere buyers. Product-driven loyalty ensures that the customer experience extends beyond service and marketing into the very offerings themselves.
5. Data-Driven Segmentation and Lifecycle Management
Finally, leveraging customer data strategically is essential. By segmenting customers according to behavior, value, and lifecycle stage, businesses can tailor offers, communication, and experiences that resonate.
Lifecycle logic helps identify at-risk customers, prompting proactive engagement to prevent churn. This data-driven approach allows companies to maximize customer retention, enhance satisfaction, and allocate resources effectively across service, marketing, and product teams.
Why Customer Loyalty Is Important in Business Growth
Customer loyalty is no longer just a nice-to-have; it is a fundamental driver of sustainable business growth. A customer loyalty business model transforms satisfied buyers into long-term revenue sources, ensures steady cash flow, and strengthens your competitive position. By understanding your customers, delivering consistent positive experiences, and fostering engagement, businesses can turn loyalty into a strategic advantage.
Retention Beats Acquisition Every Time
While acquiring new customers is essential for growth, research shows that retaining existing customers is far more cost-effective. Marketing campaigns, advertising, and onboarding processes require substantial investment, whereas loyal customers often repeat purchases with minimal prompting.
By focusing on retention, businesses can maximize lifetime value and reduce churn. Additionally, loyal customers are more likely to explore other products or services, increasing cross-selling opportunities. In essence, retention acts as the backbone of revenue growth, ensuring your investment in happy customers pays off consistently.
Turning One-Time Buyers into Long-Term Revenue Streams
A customer loyalty business model emphasizes converting casual buyers into long-term customers. By engaging customers beyond the initial purchase through personalized offers, customer feedback, and consistent service, businesses can encourage repeat engagement.
This approach not only generates steady revenue but also allows companies to plan inventory, marketing, and development more effectively. For example, personalized communication based on purchase history or preferences shows that you understand your customers, prompting them to return and invest more in your brand over time.
How Loyal Customers Keep Your Cash Flow Steady
Loyal customers are predictable revenue sources. Unlike one-time buyers, they create recurring income streams that stabilize cash flow, enabling businesses to make strategic investments without the pressure of constant acquisition.
Repeat business from satisfied customers reduces volatility, allowing companies to forecast revenue more accurately and optimize customer retention strategies. This stability is especially critical for subscription-based models, service industries, and seasonal businesses, where predictable engagement from loyal clients can make or break financial planning.
The Power of Word-of-Mouth Loyalty
Loyal customers are not just consistent buyers—they are brand advocates. They generate word of mouth that attracts new prospects at no additional marketing cost. Positive recommendations from trusted sources are far more persuasive than advertisements, and loyal advocates often influence peers to explore your offerings.
Businesses that cultivate customer satisfaction and memorable experiences tap into this powerful network effect, expanding their customer base organically. In fact, companies with strong word-of-mouth influence often outperform competitors, even with smaller marketing budgets.
Competitive Advantage Through Emotional Connection
True loyalty goes beyond transactions; it is rooted in emotion. Customers remain loyal when they feel valued, understood, and connected to a brand. By fostering strong customer relationships, businesses create an intangible competitive advantage.
Emotional connections drive advocacy, repeat purchases, and resilience against competitors’ pricing or promotional strategies. Brands that invest in building these connections through personalized service, co-created products, and attention to customer feedback establish a lasting bond that transactional loyalty alone cannot achieve.
4 Key Loyalty Program Architectures
Points-Based Programs
Designing a loyalty program is more than simply issuing points or discounts; it requires aligning rewards with customer expectations, business objectives, and operational capacity. Points-based programs are the most familiar type. Customers earn points for every purchase or interaction, which they can redeem for products, discounts, or exclusive experiences. This system is simple and widely understood, encouraging repeat purchases and frequent engagement.
However, it can sometimes feel purely transactional, reducing emotional connection if rewards are generic or predictable. Companies like Sephora go beyond the basics by offering points not only for purchases but also for early access to exclusive events, blending transactional incentives with personalized experiences that make customers feel valued and appreciated.
Tiered-Based Programs
Tier-based programs add sophistication by structuring rewards across levels based on engagement or spending. Customers progress through tiers, with higher levels offering more exclusive perks. This approach motivates long-term customers to increase interaction and fosters a sense of achievement and prestige.
However, poorly designed tiers can frustrate customers who struggle to reach higher levels or feel excluded from benefits. To be effective, tiered programs must combine clear communication and personalization, ensuring customers understand the value of progressing through the system and feel consistently rewarded for their loyalty.
Membership-Based Programs
Membership-based programs take loyalty further by offering exclusive access, benefits, or services to paying or registered members. They often involve subscription fees, generating predictable revenue while deepening emotional connection. Programs like Amazon Prime demonstrate how convenience, early access, and unique perks make customers feel that membership is indispensable.
For these programs to succeed, the perceived value must clearly exceed the cost; otherwise, they risk appearing restrictive rather than rewarding. Membership programs excel at fostering community and long-term engagement, encouraging repeat business and stronger customer relationships.
Value-Based Programs
Value-based programs focus on aligning loyalty incentives with customer values, such as sustainability, charitable contributions, or ethical practices. These programs create a deeper emotional connection, enhancing customer satisfaction and fostering word-of-mouth advocacy.
Brands like Patagonia and TOMS integrate cause-driven initiatives into their loyalty systems, allowing customers to feel their purchases contribute to a greater purpose. While harder to scale and appealing to a subset of long-term customers, value-based programs create powerful engagement that often translates into sustained loyalty and brand advocacy.
5 Approaches to the Customer Loyalty Business Model
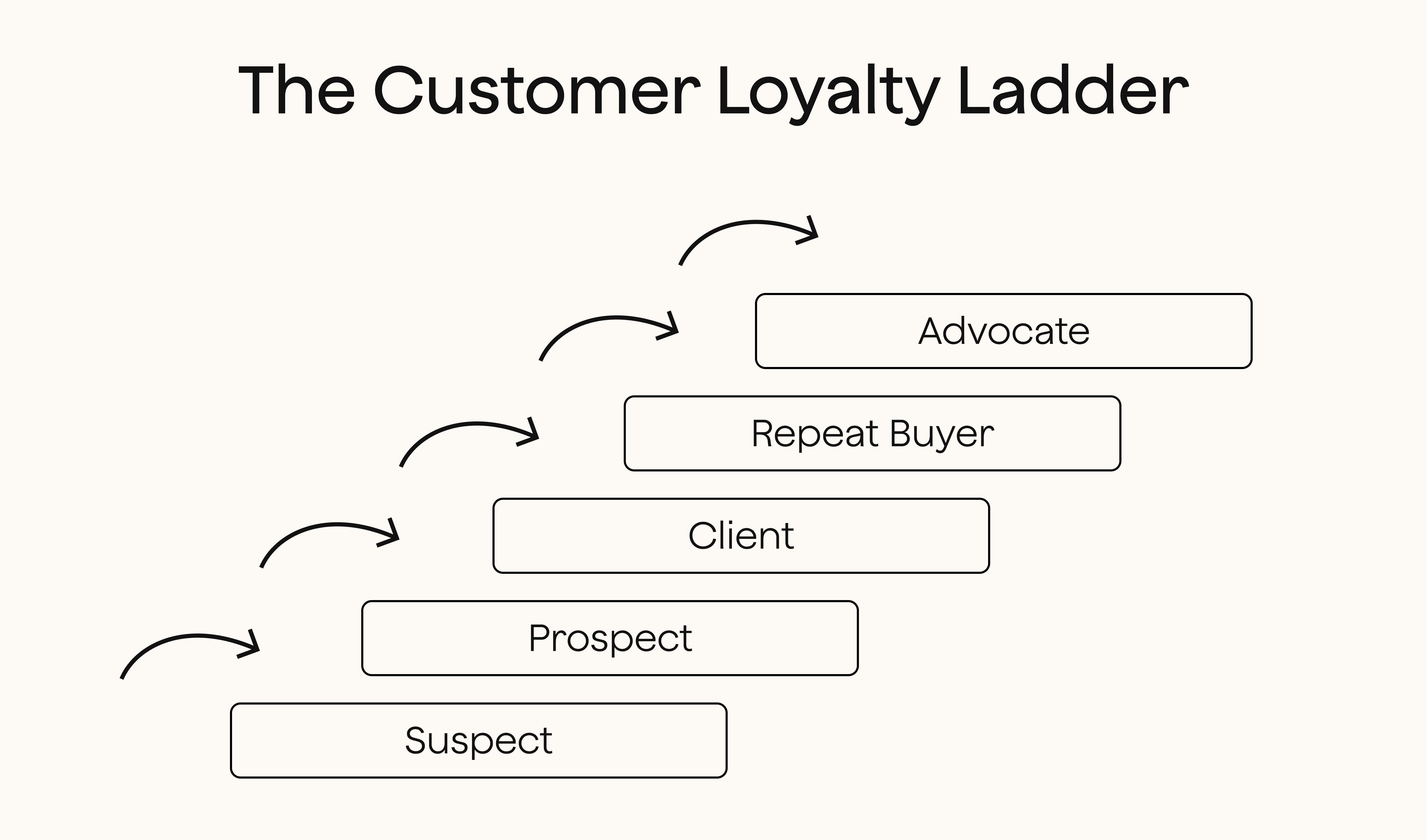
Loyalty Ladder
The Loyalty Ladder is a framework that visualizes the journey of a customer from initial awareness to full brand advocacy. At the base, customers are one-time buyers who may not yet feel any emotional connection to a brand. As businesses engage them through personalized experiences, quality service, and consistent customer satisfaction, they move up the ladder to become regular purchasers.
The highest rungs represent long-term customers who actively recommend the brand and contribute to word-of-mouth growth. This approach emphasizes that loyalty is a progressive process requiring continuous engagement, feedback, and adaptation. By monitoring where customers are on the ladder, companies can tailor strategies to foster deeper relationships and ensure repeat business.
Apostle Model
The Apostle Model identifies highly loyal customers who actively promote the brand to others. Apostles are not just satisfied buyers; they are advocates who amplify positive experiences across their networks. Businesses that can recognize and engage apostles benefit from organic growth and enhanced brand credibility.
Developing apostles requires consistent customer experience excellence, personalized communication, and frequent feedback to understand what motivates advocacy. Companies that fail to nurture apostles may see their most passionate customers drift away, losing both repeat purchases and influential promotion. This model highlights the value of turning satisfaction into proactive engagement, making loyalty a strategic tool rather than a passive outcome.
Rai Srivastava’s Model of Customer Loyalty
Rai Srivastava’s Model focuses on the interplay between satisfaction, trust, and switching costs to predict customer retention. According to this framework, loyal customers are those who perceive high value from their relationship with a brand, trust the company, and experience barriers to leaving, whether through convenience, emotional attachment, or repeat business incentives.
Implementing this model involves measuring customer feedback, segmenting existing customers by value and engagement, and creating interventions that strengthen trust and reduce churn risk. It provides a structured, data-driven approach to understanding loyalty, ensuring businesses can act strategically to retain high-value customers while enhancing overall customer relationships.
Commitment–Loyalty Model
The Commitment–Loyalty Model emphasizes the emotional and psychological dimensions of loyalty. Customers remain committed to brands that consistently meet expectations, deliver positive experiences, and make them feel understood. This model highlights that loyalty is not solely a result of rewards or incentives but also of emotional connection.
Businesses applying this approach focus on fostering engagement through attentive service, recognition, and tailored interactions, ensuring customers feel valued at every touchpoint. While commitment-driven loyalty can be harder to measure quantitatively, it often translates into long-term customers who are resistant to competitor offers and actively advocate for the brand.
Two-Dimensional Model of Customer Loyalty
The Two-Dimensional Model combines attitudinal and behavioral perspectives to provide a holistic understanding of customer loyalty. Behavioral loyalty measures repeat purchases and engagement, while attitudinal loyalty assesses satisfaction, trust, and emotional attachment. By analyzing both dimensions, businesses gain deeper insights into customer retention, segmenting high-value customers who are emotionally invested versus those who are purely transactional.
This model encourages companies to design strategies that strengthen both dimensions—enhancing customer experience to boost emotional loyalty while ensuring operational excellence and rewards systems maintain repeat business. Integrating feedback and data-driven insights ensures that loyalty is actionable, measurable, and tied directly to growth outcomes.

RFM Model (Recency, Frequency, Monetary Value)
The RFM Model is a data-driven approach to customer loyalty that segments customers based on their purchasing behavior. It evaluates three key dimensions: recency, how recently a customer made a purchase; frequency, how often they buy; and monetary value, how much they spend over time. Customers who score highly across these dimensions are considered more loyal and valuable to the business.
This model allows companies to identify loyal customers objectively rather than relying on perceived satisfaction or emotional attachment. By ranking customers based on transactional data, businesses can prioritize retention strategies, personalize marketing efforts, and allocate resources more efficiently. High-RFM customers may receive exclusive offers or early access, while lower-RFM segments can be targeted with re-engagement campaigns.
Conclusion
A customer loyalty business model is far more than a marketing tactic; it is a holistic strategy embedded across every department, from service and product development to marketing and operations. By combining personalized experiences, frequent customer feedback, and thoughtful rewards, businesses can turn casual buyers into long-term customers who drive repeat purchases and advocate through word of mouth.
Loyalty strengthens customer relationships, stabilizes cash flow, and provides a competitive edge through emotional connection. Companies that prioritize retention, understand their customers, and deliver consistent value create sustainable growth and ensure that happy customers remain the cornerstone of success.



